Why China's technology industry is up in arms over work schedule
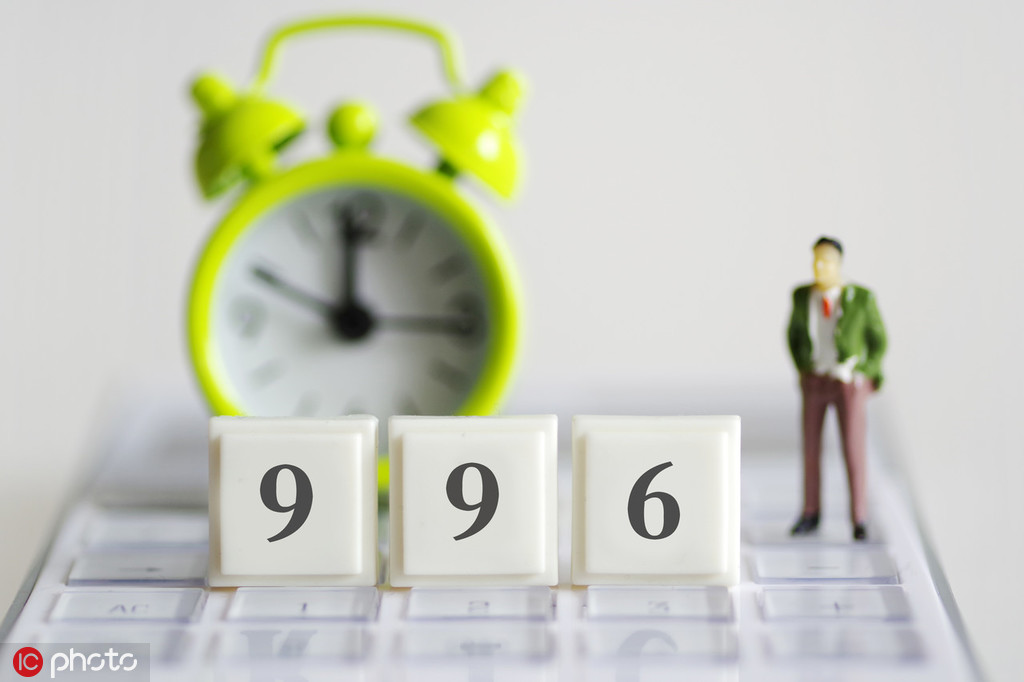


A work schedule dubbed"996"-from 9 am to 9 pm, six days a week - went viral overnight on China's cyberspace.
The incident first surfaced last week as Chinese coders openly expressed their weariness over the de facto unpaid overtime - an industry malaise - by creating a project called 996.ICU. The grim joke suggested that by conforming to such a relentless work culture, one risks ending up in an intensive care unit.
Apparently, complaints have escalated into a broader debate on work-life balance, a rarity, or even a luxury for Chinese tech workers in the cutthroat competition for users and capital.
The problem is by no means new. China's Labor Law stipulates that employees shall work for no more than eight hours a day and no more than 44 hours a week on average. Besides, employees working weekends should be paid double time.
But the timing for the routine-turned-crisis is carrying conspicuously more weight. So the question becomes: Why now?
To me, the issue is reminiscent of a set of concepts in the political science realm. Scholars have proposed that societies behave cyclically in governing themselves with different types of governmental legitimacy, among which one common type is known as "instrumental legitimacy".
This source of legitimacy rests on the rational assessment of the usefulness of an authority, and is very much based on the perceived effectiveness of service delivery.
In simple words, a body manages to maintain its authority when there are largely beneficial consequences or utility gains. But when it fails to live up to expectations, questions arise over its source of legitimacy.
A reality check on China's internet sector using the very same lens arrives at a similar conclusion. In the past few years, China's quest to transform its economy to one that is innovation-powered has fueled the miraculous rise of a torrent of internet giants and tech unicorns.
They have dwarfed multinational corporations and become the "greener pasture" in the country's job market. Generous paychecks, stock options and the allure to achieve "financial freedom" in one's late 20s have collectively compensated for the expected long working hours. In fact, thanks to the tech boom, China has indeed turned out the highest number of new millionaires worldwide (a lot of them being entrepreneurs and software developers), according to multiple surveys.
But as the economy slows down, business stagnates, venture capital drains and layoffs begin - i.e. all the past euphoria and "legitimacy" subside - are Chinese millennials still going to give the nod to the previous pact?
When the dot-com bubble burst in the 2000s, working hours in Silicon Valley were effectively shortened as people pursued a better work-life balance. Well, history doesn't repeat itself but it does rhyme. Therefore, the backlash against the grueling 996 work schedule isn't surprising.
China always has this reputation for a work culture that tends to prioritize work over life. Many tout it as a virtue and a necessity, given the nation's unchanged status as the world's largest developing economy. Alibaba's Jack Ma says it's "a huge bliss to get to work 996", adding his organization doesn't need to hire people who look forward to a typical eight-hour office lifestyle.
At the end of the day, it's a matter of choice. But it does no harm to distinguish if 996 is a means or an end in itself. If the work ethic stands for expedited deadlines, it's heartening news to both the organization and the individual. But if the motto is simply a mirage of camaraderie and a result of peer pressure, then tech workers do face the danger of burnout, physically and mentally.
I am not in the tech circle but as a journalist and writer, I work"996", or even"696" from time to time. The only motivation is because I want to and I know clearly what I want from this stage of my life.
But there is one thing I am sure of: China's pursuit of higher-quality growth means that any industry, especially technology, shouldn't be one featuring labor-intensive. It should be a creative industry, and creativity usually finds its roots in life.