Robotics sector goes full throttle for self-reliance despite headwinds
Critical components manufactured at home gradually replacing imports


With breakthroughs in critical technologies, China's robotics industry is gaining significant momentum as it strides ahead, experts and industry insiders have said.
Qiao Hong, an academician at the Chinese Academy of Sciences and director of a laboratory of multimodal artificial intelligence systems, said domestic humanoid robots have seen continuous technological advancements — in fields from component manufacturing and machine tool processing to control systems — and are now aligning with internationally advanced standards.
For example, in manufacturing, critical components are gradually replacing imports while achieving comparable levels of precision, especially in industrial applications, she said.
"By combining these technologies with well-developed, independently built robotics supply chains, the country has established a solid foundation for final complete system integration," Qiao added.
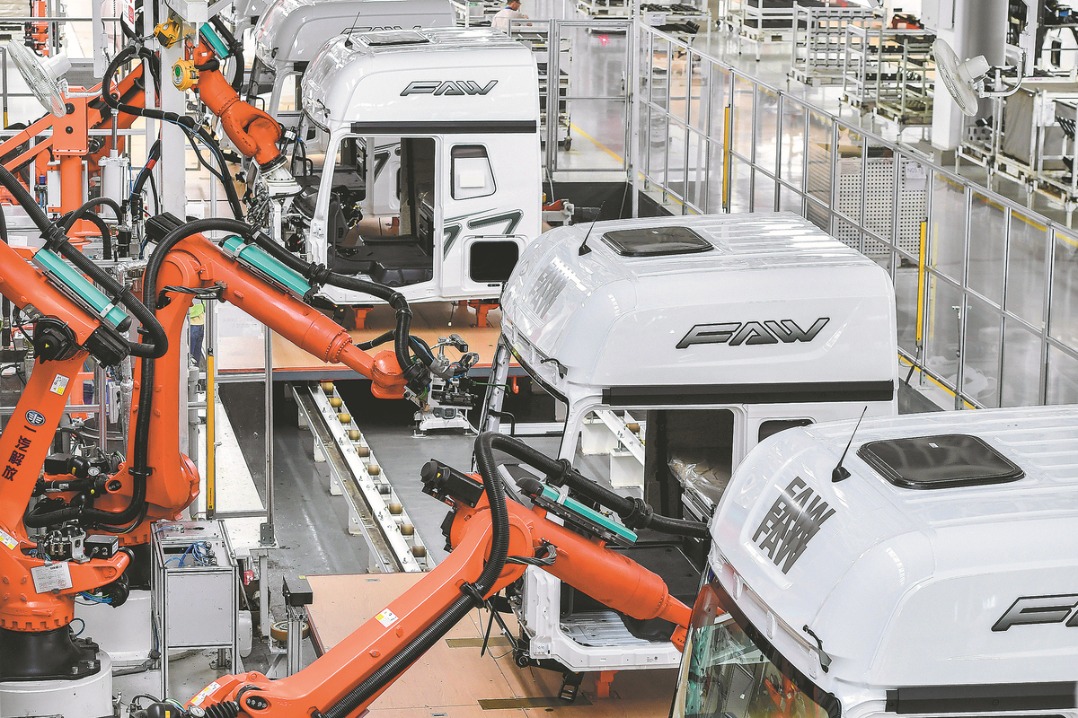
"Over 95 percent of the components in our full-size humanoid robots are now domestically produced," said Zhang Dapeng, an executive at Shenzhen, Guangdong province-based humanoid robotics company Leju (Shenzhen) Robotics Co Ltd.
This is a result of accumulated technological breakthroughs and a stable domestic supply chain, Zhang said.
With the delivery of its 100th full-size humanoid robot in January, Leju Robotics has turned itself into a global leader in terms of announced delivery volume. The company said it expects to deliver approximately 1,000 units this year.
However, achieving higher precision in complete humanoid robot systems still requires further breakthroughs in integrated platform technologies that usually involve AI, perception technology, and even brain science, Qiao noted.
"Making humanoid robots act more like humans calls for the integration of unit and generalized technologies, as well as that of traditional automation knowledge and brain-inspired intelligence," she said.
Qiao said brain-inspired intelligence is used to mimic human characteristics from the inside out, designed to replicate human mechanisms and structures and to achieve higher levels of performance and humanlike behaviors.
"We analyze key regions of the human brain to bring the perception and attention mechanisms of humanoid robots closer to those of humans," she said, explaining that brain-inspired intelligence grants humanoid robots greater flexibility and reliability, enabling more fluid and natural movements.
Incorporated with brain science, AI and more, the country has successfully developed an integrated software platform for humanoid robots, the first of its kind in the world, the academician said.
Called "mega factory", the platform is designed to improve hardware performance through software simulations, eliminating the need for physical manufacturing and instead using AI-driven simulations to predict potential hardware system issues. It can, therefore, help accelerate design optimization, streamline upgrades, enhance overall robotic performance and speed up iteration cycles, Qiao explained.
Looking ahead, while the mass production of cost-effective but relatively low-performance and low-precision robots is now a reality, the challenges extend beyond large-scale manufacturing, the academician said.
"For specialized and major scenarios in industries such as manufacturing, agriculture, services and healthcare — where robots must meet stringent demands for performance, precision, reliability and safety — widespread deployment will still take time," she noted.