Sci-tech helps protect South China biological treasure trove


GREEN PEARL
As a key participant in global ecological conservation, China continues to explore innovative approaches to biodiversity protection and ecosystem management.
Dinghushan National Nature Reserve, a model of ecological conservation in China, is not only the country's first nature reserve but also an important member of UNESCO's World Network of Biosphere Reserves. Its successful experience offers valuable lessons for global ecological conservation.
Located in Zhaoqing, Guangdong province, the 1,133-hectare reserve, established in 1956 and managed by the SCBG, is hailed as the "Green Pearl on the Tropic of Cancer Desert Belt," due to its exceptional ecological value and striking contrast with the typically arid regions along the Tropic of Cancer.
In 1979, it became one of China's first three biosphere reserves under UNESCO's Man and the Biosphere (MAB) program.
Xia Hanping, director of the reserve, noted that its primary focus is protecting South Asian subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forests and their wildlife. Forest coverage in the reserve has remained around 98 percent, with 68 state-protected plant species and 73 protected animal species found there.
Populations of key protected species have either remained stable or increased significantly — while the area of subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forests has grown by over 70 percent since the reserve's establishment, Xia said.
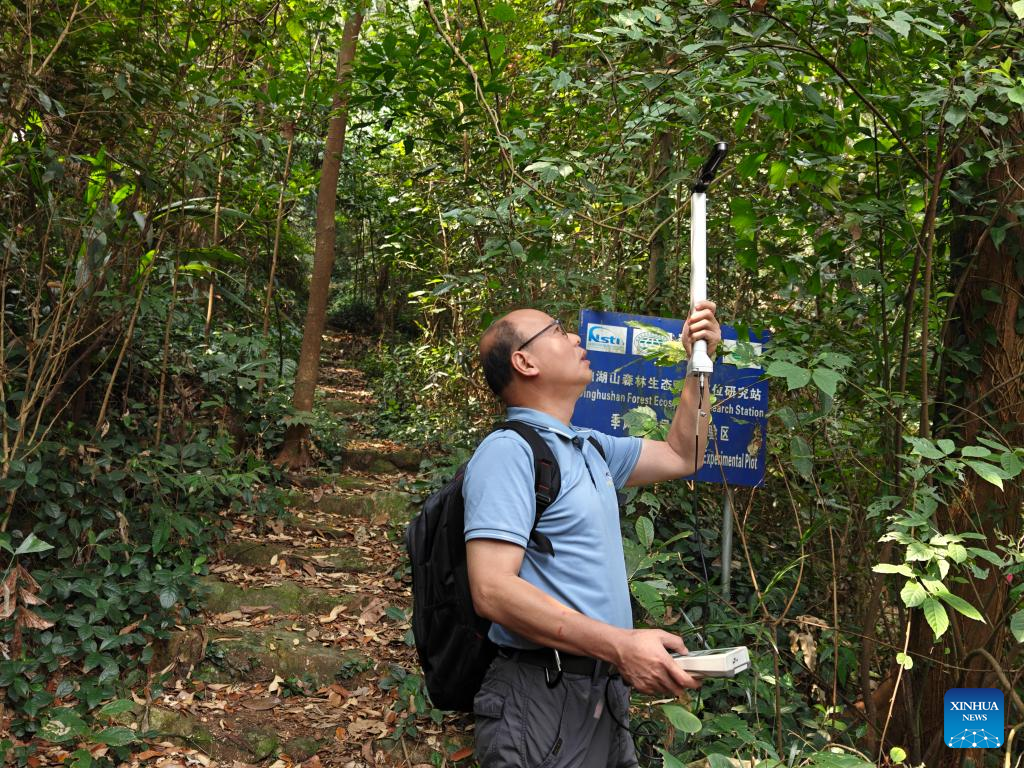
Liu Juxiu, head of the Dinghushan research station, revealed that the reserve serves as a natural laboratory for scientific research.
Based on nearly two decades of investigation, researchers have found that previous estimates, relying primarily on forest above-ground biomass and surface water in carbonate rock regions, have led to a significant underestimation of China's terrestrial carbon sequestration capacity, with this miscalculation amounting to as much as 50 percent. The study further reveals that terrestrial carbon sinks across China are highly sensitive to regional environmental variability.
Scientists have also assessed the current state and temporal dynamics of carbon sequestration in China's forest ecosystems, providing estimates of forest carbon stocks and revealing considerable remaining sequestration potential. In examining ecosystem responses to global change, they have identified the mechanistic pathways through which nitrogen deposition modulates soil carbon emissions in tropical forests, and have further elucidated the biogeochemical cycles of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus under climate warming.
Chu Guowei, deputy director of the Dinghushan research station, said that the station collaborates with research institutions in over 20 countries, including the United States, Australia, Canada, Germany, France, Sweden, Denmark, Japan and Kenya — thereby advancing multiple ecological studies.
The reserve's success lies not only in conservation but also in harmonizing humans and nature. In 2024, the Ministry of Natural Resources adopted a proposal by Ren Hai, director of the SCBG, to retain high-quality farmland within the reserve. "Preserving farmland supports local livelihoods while providing food and habitat for wildlife, achieving a win-win balance between conservation and development," Ren said.
Wang Ding, secretary-general of China's MAB National Committee, noted that nature reserves should act as bridges for socio-economic development, not barriers. "The philosophy of harmonizing humans and nature aligns well with China's realities."
- Sci-tech helps protect South China biological treasure trove
- Senior CPC official urges sound implementation of governance policies for Xinjiang
- Mountain fire breaks out in North China province
- Robots revolutionizing risky mining operations
- Ecological restoration brings economic return
- Old mines given new purpose