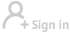Backgrounder: US presidential elections
 |
|
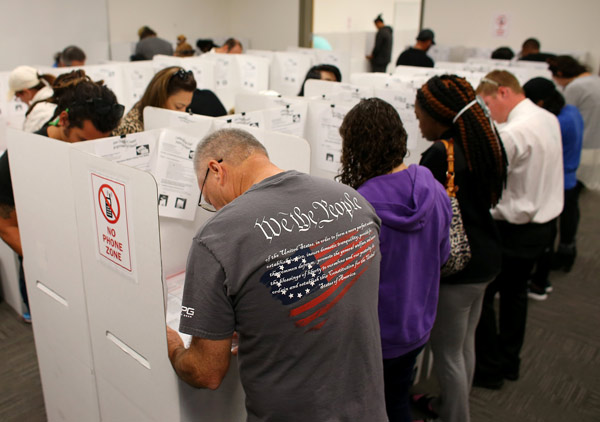
A voter wears a shirt with words from the United States Constitution while casting his ballot early as long lines of voters vote at the San Diego County Elections Office in San Diego, California, US, November 7, 2016. [Photo/Agencies] |
Starting in 1792, US presidents and vice-presidents have been elected quadrennially on the Election Day, the first Tuesday after the first Monday of November.
US voters only cast their ballots for a slate of electors of the US Electoral College, who in turn elect the president and the vice-president.
The current US presidential election system, featuring the Electoral College, was originally established by Article Two of the US Constitution, as a result of a compromise between those who wanted the US Congress to choose the president and those who preferred a national popular vote.
The whole process of the presidential election can be divided into four phases, namely, the primary elections, the nominating conventions, the presidential nominee campaigns and the national vote.
During the nomination race, usually from January to June of an election year, primaries and caucuses are held in 50 states, the District of Columbia and all US territories, to elect a presidential nominee for each major political party.
After securing the party nomination, each party's de facto presidential nominee chooses a vice presidential nominee to run with him or her. The pair receive their official nominations at their party's national conventions, which take place during the summer of the election year.
Between the conventions and the Election Day, all presidential candidates run their campaigns nationally, holding rallies, running ads and giving interviews. They have to repeatedly adjust and state their policies and stances to address concerns of voters at home and abroad, and face challenges from rivals. They also face off in televised debates, usually three times between presidential candidates and one between vice presidential candidates.
As hundreds of millions of US dollars are needed to sustain the protracted campaign cycle, candidates have to exert themselves to collect political donations throughout the election year.
Voters can either cast their ballots prior to or on the Election Day, depending on different voting laws of each state, or send in their ballots by mail. But the ballot is actually voting to select the electors.
Under the US Constitution, the number of Electoral College electors for each state is equal to the number of its Senators and Representatives in the US Congress. The District of Columbia, which has no congressmen, is granted three electors. US territories are not represented in the body.
All states except Maine and Nebraska employ the "winner-takes-all" system, meaning whichever ticket wins the popular vote wins all of the state's electoral votes. Any pair of presidential and vice presidential candidates who gain at least 270 electoral votes of the total 538 are claimed the winners.
In Maine and Nebraska, the electoral votes are divided between the candidates depending on the result of the state's popular vote.
Although the president-elect and vice-president-elect usually can be yielded on the Election Day, the official voting for them by the Electoral College is held on the first Monday after the second Wednesday in December.
If no presidential candidate wins at least 270 electoral votes, the House of Representatives will choose the president and the Senate the vice president.
The new president and vice president are supposed to be sworn in on Jan. 20 of the following year. In case the House of Representatives has not chosen a president-elect by that date, the vice president-elect becomes the acting president until the floor makes the decision. If the vice president-elect is also not known by then, the sitting House Speaker becomes the acting president.
In addition to candidates from the Democratic and Republican parties, several small political parties also put their candidates' names on the ballot. However, mainly due to the "winner-takes-all" policy, US electoral politics is still dominated by the two major parties.